Access Keys
Access keys play a crucial role in granting permissions to Mission Controls, Satellites or Analytics within Juno.
When you sign in to Juno's Console using Internet Identity, you — and no one else (including not Juno) — become the owner of your mission control. This information is then sent back to your browser, where you can manage your modules.
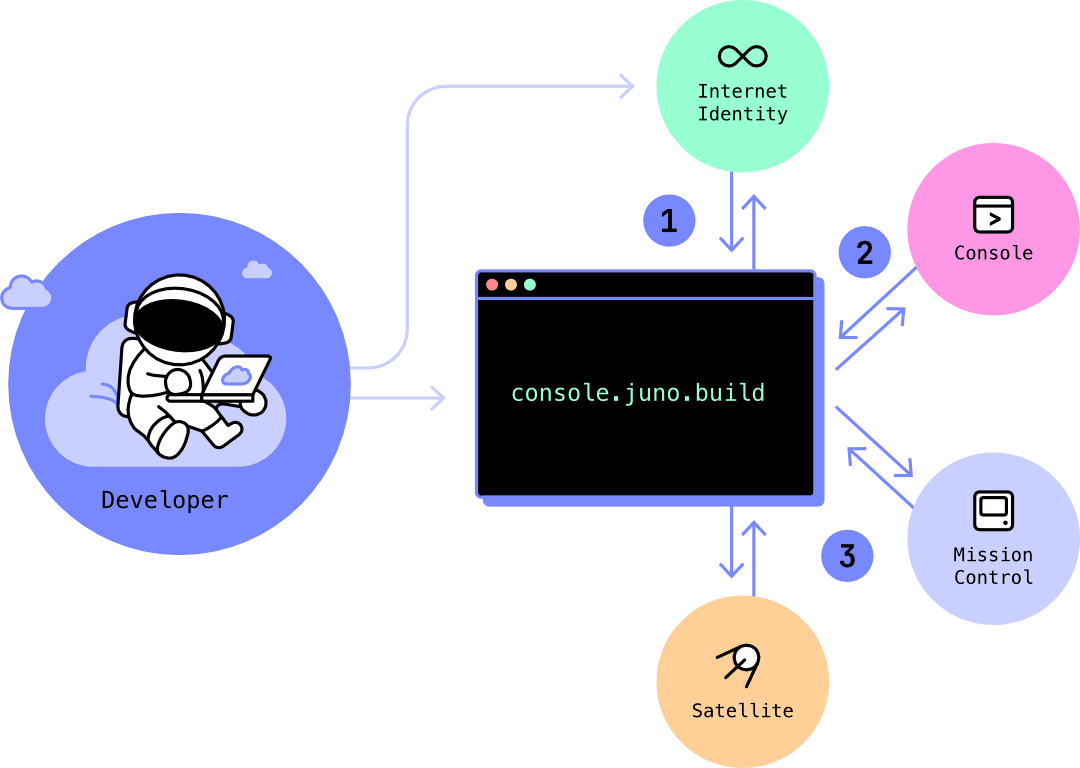
When you create a satellite, you and your mission control become its owners. Per extension, you — and no one else (including not Juno) — own your satellite.
- What was previously referred to as controllers in earlier versions of the documentation is now called administrative access keys. The concept remains the same — only the terminology has been updated for clarity and consistency.
- One access key is identified by a principal.
Roles
Each access key is assigned a role that defines what it can do:
| Role (Internal) | Display Name | Can Submit | Can Apply/Commit | Can Deploy Immediately | Can Upgrade Immediately |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admin | Administrator | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Write | Editor | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Submit | Submitter | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
An administrator can perform tasks such as configuring or deploying an app, topping up a mission control or satellite, creating a new collection in the datastore or storage, or configuring a custom domain in the hosting.
An editor can publish new serverless function versions to a Satellite’s CDN, deploy your frontend application, and read data from a collection. However, it cannot directly upgrade a Satellite or start/stop a module.
A submitter can propose changes—such as publishing a new version of a serverless function or frontend app—but those changes must be manually reviewed and applied using the Console UI or CLI.
Generating Access Keys
You can generate additional access keys to allow other developers, services, or CI pipelines to interact with your modules. When doing so, you can assign a role based on the level of access required.
Access keys can be generated either through the Console UI or using the CLI.
You can generate a limited number of administrator access keys for a single module, in line with the limitation set by the Internet Computer.
To accomplish this, you have two main options.
When creating a new Satellite, it’s very likely that you’ll want to generate access keys for local development or to enable automated deployments from CI. Check out the guides:
Generate an Access Key with the Console UI
You can generate and manage access keys through the Console:
- Go to http://console.juno.build and select your module (Satellite, Analytics or Mission Control)
- Open the Setup tab
- Scroll to the Access Keys section and click Add an access key
- Choose Generate a new access key
- Select the desired role (e.g., Administrator)
- Click Submit
You can also manually enter an access key instead of generating one, if you wish to reuse an existing one.
Generate an Access Key with the CLI
When using the CLI, you can either reuse an existing access key or generate a new one.
Reuse an existing access key
When setting up an additional Satellite, you might want to reuse an existing access key already configured on your local machine. To do this, simply run:
juno login
and follow the instructions.
When you run the command, the CLI checks if an access key is already present on your machine. If found, it will give you the option to either reuse the existing key or generate a new one. If you choose to reuse it, the CLI will guide you through the process.
Generate a new access key
To generate a new access key and attach it to your desired Mission Controls and Satellites, you can run:
juno login
The CLI will guide you through the process.
This method is useful if you want to generate a completely new key and apply it across all your modules.
This action will overwrite the previously saved key used to configure your local CLI environment.