Datastore
The Juno Datastore offers a simple key-value model, organized by collections containing documents, for managing structured data.
Use it for structured data like user profiles, tasks, settings, or other data of your app stored as documents inside collections.
For binary files like images or files, use the Storage instead.
How does it work?
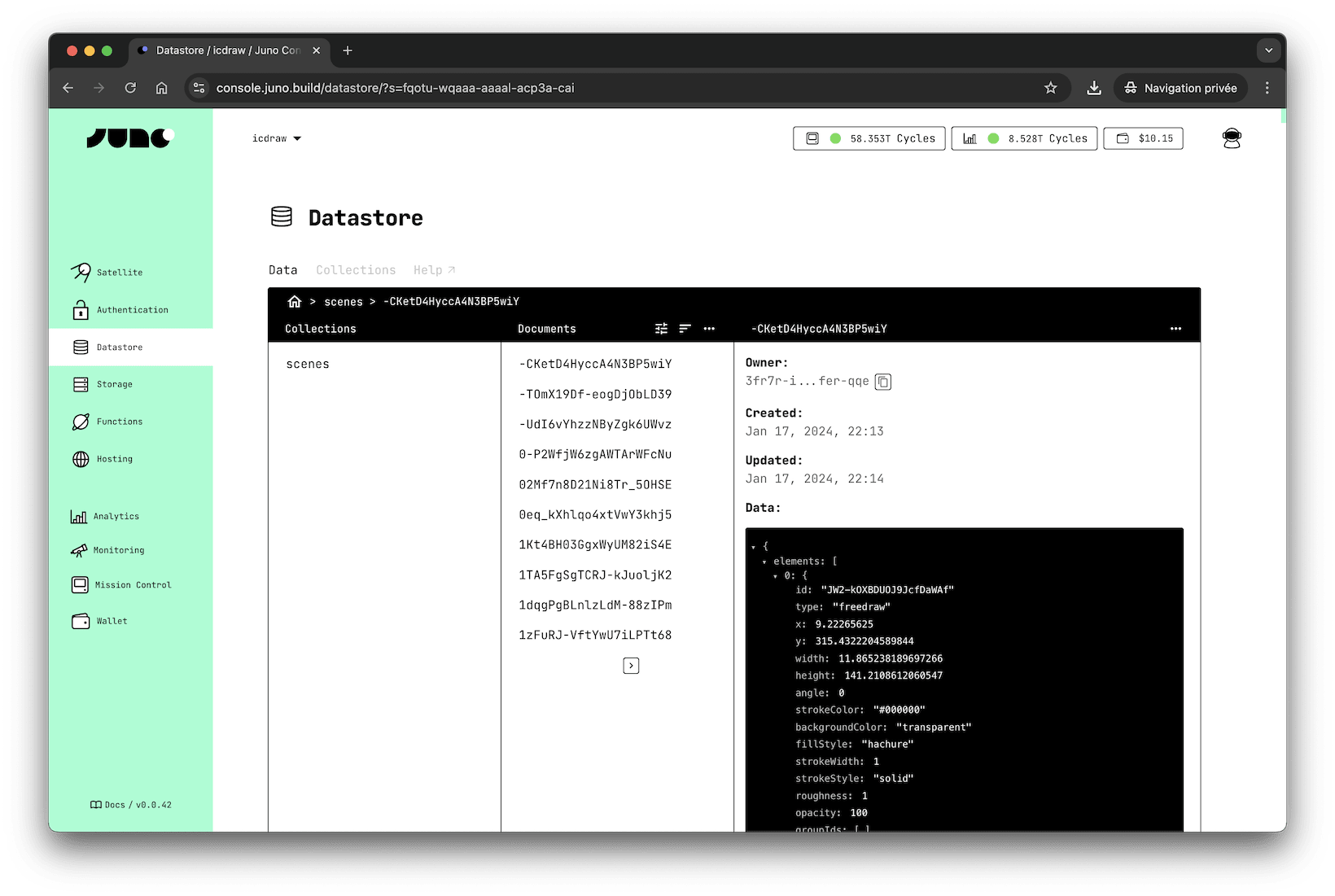
Each satellite you create has a "Datastore", which can have as many collections as you wish.
A collection contains a list of documents, each identified by a textual key that you define.
Each document is a record that holds the data you want to persist, along with timestamps (created and last updated), an associated owner (the creator of the document), and a version.
The version is used to prevent data from being overwritten, and the associated owner is used to grant read and write permissions.
Each document is identified by a key (unique within a collection).
In essence, a "Datastore" functions as a keypair store.
Limitation
Each Satellite has specific memory limits. For detailed information, please refer to the related documentation page.
As for documents, they can be up to 2MB in size. However, larger files can be saved in the storage.
Configuration
The Datastore supports various configuration options to fine-tune its behavior, such as resource limits and operational constraints. For a detailed explanation of all available options, see the configuration section.
Datastore vs Storage
Juno gives you two ways to persist data. Both follow a collections-based architecture, but they serve different purposes and behave differently in practice.
| Feature | Datastore (Structured) | Storage (Files) |
|---|---|---|
| Use case | App state, user profiles, config | Images, files, generated user content |
| Data format | JSON-like documents | Binary files |
| Identifier | key (string you define) | fullPath (auto or custom) |
| Accessible via web URL | No | Yes |
| Size limit | Max 2 MB per document | Chunked; limited by available Satellite space |
key vs fullPath
Both Datastore and Storage use a unique identifier per item — but they refer to different things and are used differently.
-
Datastore →
key:- A unique string you assign to each document within a collection.
- Used to retrieve, update, or delete a specific document.
- Commonly a UUID (e.g.
crypto.randomUUID()), a nanoid, or any meaningful string like a slug or user ID. - Example:
bafkb4by...,user:42, orconfig/theme.
-
Storage →
fullPath:- The full path of an asset used to build a valid web URL.
- It's automatically generated from the uploaded filename unless explicitly set.
- The
fullPathmust include the collection name (except for your app's frontend assets like HTML, JS, etc.). - Used to serve, list, or delete files.
- Example:
/images/logo.png(collection:images) or/avatars/user42/profile.jpg(collection:avatars).