Authentication
Juno provides a secure, passwordless authentication framework built directly into your project. It supports multiple providers out of the box, including:
- Google - secure and familiar login
- GitHub - the login your developers already use
- Internet Identity - decentralized, privacy-preserving authentication
- Passkeys - passwordless, device-native authentication using WebAuthn
It integrates seamlessly with your Datastore and Storage to power the rich features you are building.
Whether you need decentralized login, device-native passkeys, or a familiar OAuth-based sign-in, Juno - by extension your project and its Satellite - handles the complexity for you so you can focus on your app instead of managing user accounts, sessions, and sensitive data.
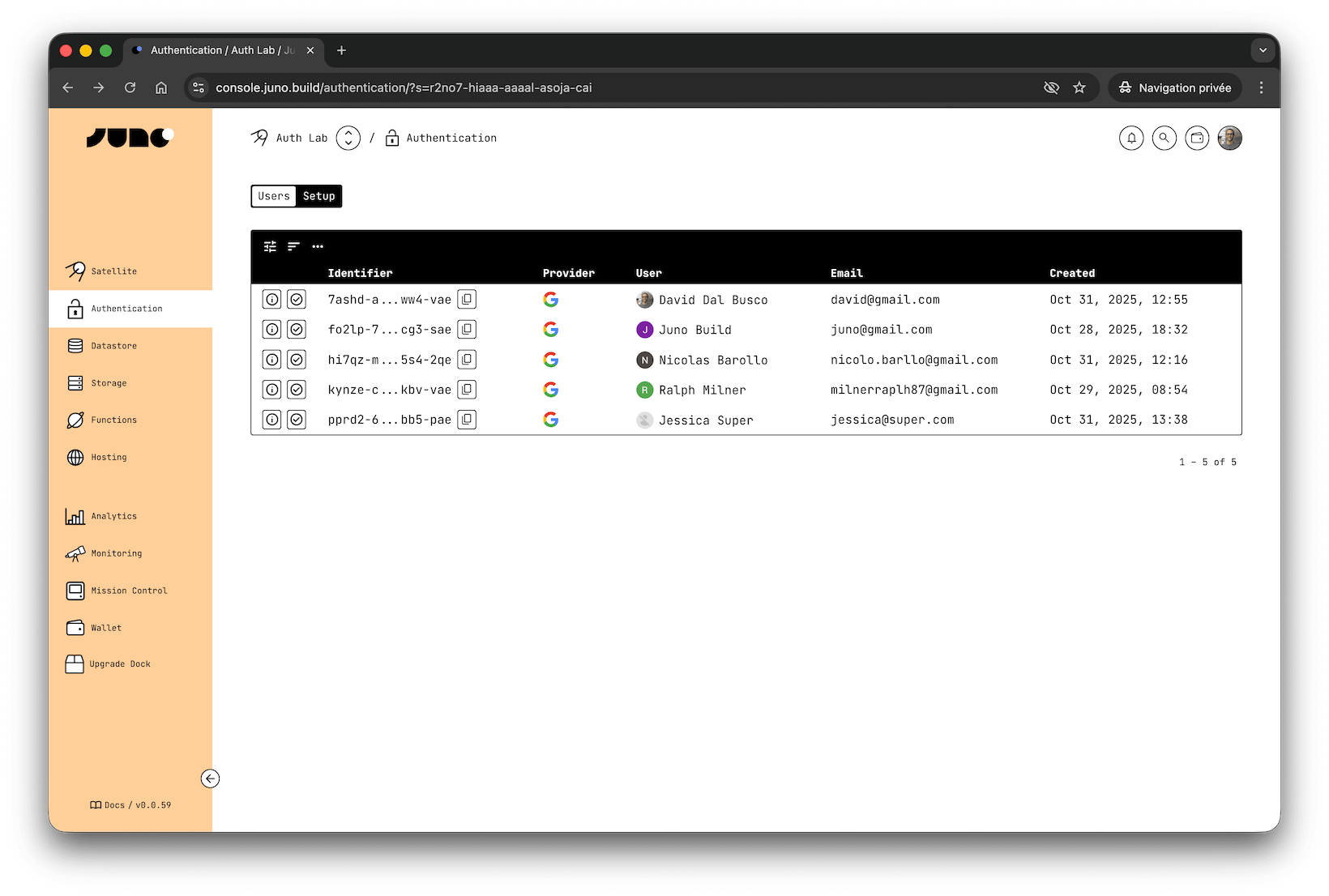
You can view and manage your users anytime in the Authentication
User Identity
When someone signs in to your app, they get an identity.
That user identity is what ties them to the data they create and the actions they take.
Identities are scoped to your app - users can't be tracked across other sites or services.
Depending on the sign-in method and what the user consents to, your app may also receive basic profile metadata such as a name or email address.
Domain-Based Identity
For privacy reasons and to prevent tracking across sites, a user's identity is tied to the domain where they sign in.
Passkeys
With Passkeys, the identity is linked to the hostname the user signs in on. It works for that domain and its subdomains.
For example, a passkey created on hello.com will also work on www.hello.com, but not on a different domain like world.com.
You can change this in the sign-up options if you want it to cover a different domain than the one read from the browser's URL. For example, you may want to use the top-level domain when signing in on a subdomain. You cannot specify a totally different domain.
Choosing a Provider
Each authentication method has its strengths. The right choice depends not only on your app's technical needs, but also on what your users expect and feel comfortable with.
-
Google:
- ✅ Familiar and frictionless login with a trusted provider.
- ✅ Works across devices and browsers in all your applications.
- ✅ Supports account recovery and multi-device sync.
- 🤔 Depends on Google's infrastructure and availability.
- 🤔 Slightly higher resource usage on your Satellite and per extension costs, since it must verify tokens issued by Google and sign identities.
-
GitHub:
- ✅ Familiar login for developer-focused apps.
- ✅ Works across devices and browsers in all your applications.
- 🤔 Requires a backend proxy to handle the OAuth flow securely.
- ⚠️ You need to self-host the Juno API or run your own compatible proxy.
-
Internet Identity:
- ✅ Fully decentralized and privacy-preserving.
- ✅ Prevents tracking between domains.
- ✅ Supports account recovery.
- 🤔 Requires a brief context switch to an external window.
- 🤔 Domain scoping requires correct configuration.
- 🤔 When users choose to sign in with a third party (Google, Apple, etc.), it also depends on their infrastructure and availability. Plus, it relies on configured credentials owned by the DFINITY Foundation.
- 🤔 Less known outside the Internet Computer ecosystem.
-
Passkeys:
- ✅ Passwordless and device-native (Face ID, Touch ID, etc.).
- ✅ Familiar Web2-like UX with strong cryptographic security. ✅ Supports multi-device sync through password managers.
- 🤔 Users must distinguish between sign-up and sign-in flows.
- 🤔 Sync depends on Apple or Google password managers and their infrastructure.
- ⚠️ Passkeys stored locally can be lost if the browser or device is reset.
Many developers combine multiple providers - for example, offering Google as the default and Internet Identity or Passkeys as alternatives.